
Chapter 11: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition - Relatively large number of sellers, differentiated products, easy entry/exit
Relatively large # of sellers
Small market shares
No collusion - The presence of a relatively large number of firms ensures that collusion by a group of firms to restrict output and set prices is unlikely
Independent action - Each firm can determine its own pricing policy without considering the possible reactions of rival firms
Product differentiation - Variations of particular product
Product attributes
Service
Location
Brand names + packaging
Some control over product prices
Easy entry + exit
Few economies of scale
Low capital requirements
Non-price competition - Product differentiation + advertising
Four firm concentration ratio - Ratio of the output (sales) of the four largest firms in an industry relative to total industry sales
Very low in purely competitive industries
Herfindahl index - Sum of the squared percentage market shares of all firms in the industry
Important to assess oligopolistic industries
Lower index → Greater chance of being competitive
Monopolistic competition’s demand curve
Highly elastic
No perfect product substitutes
Price elasticity depends on # of rivals + degree of product differentiation
Short run
Produces where MR = MC
May incur loss in short run

Long run
Only normal profit (break even)
Economic profits → Firms enter industry → Quantity increases → Economic profit decreases
Economic losses → Firms leave industry → Quantity decreases → Economic profit increases
Complications
Product differentiation can prevent duplication
In reality, entry is not as free
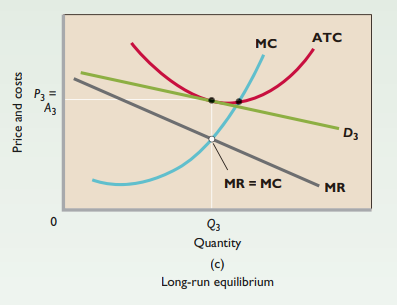
Efficiency
Neither productive nor allocative efficiency
Average total cost slightly higher than optimal
P > MC → Underallocation of resources
Excess capacity - Plant and equipment that are underused because firms are producing less than the minimum-ATC output
Product differentiation
Stay ahead of competitors
Provides more range to consumers
Trade-off b/w consumer choice + productive efficiency
Oligopoly - Market dominated by a few large producers of a homogeneous or differentiated product
3-5 firms
Homogeneous oligopoly - Standardized products
Differentiated oligopoly - Differentiated products
Strategic behavior - Self-interested behavior that takes into account reactions of others
Mutual interdependence - A situation in which each firm’s profit depends not entirely on its own price and sales strategies but also on those of the other firms
Entry barriers
Economies of scale
Large capital expenditures
Ownership + control of raw resources
Merge 2 competing firms → Increase market share + achieve greater economies of scale + greater monopoly power
Shortcomings of concentration ratios
Localized markets
Interindustry competition - Competition b/w 2 products associated w/ different industries
Import competition - Competition b/w foreign products
Game theory - Study of how people behave in strategic situations
Payoff matrix shows payoff to each firm resulting from different combinations of strategies
Collusion - Cooperation w/ rivals rather than work competitively/independently
Incentive to cheat - Cheating on collusive agreement to increase own profit
3 oligopoly models
(1) the kinked-demand curve, (2) collusive pricing, and (3) price leadership
Why isn’t there only a single model?
Diversity of oligopolies - Oligopoly encompasses a greater range and diversity of market situations than do other market structures
Complications of interdependence - The mutual interdependence of oligopolistic firms complicates matters significantly
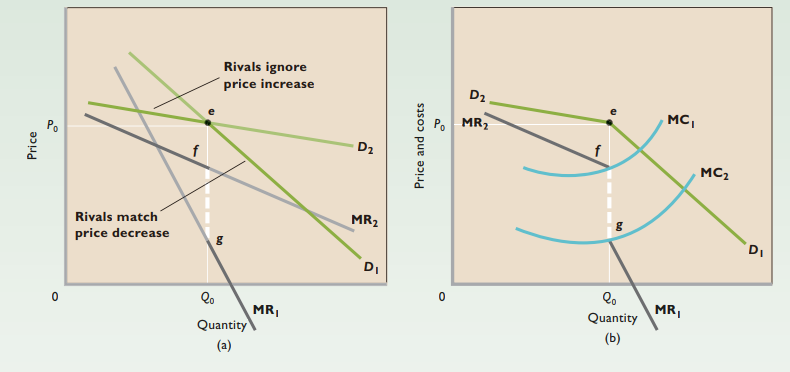
Kinked demand curve - Demand is highly elastic above the going price P0 but much less elastic or even inelastic below that price
Rivals can either match price changes or ignore price changes
Prices stable in non-collusive oligopolistic industries
Even if costs change significantly, may not need to change price
Price war - Successive and continuous rounds of price cuts by rivals as they attempt to maintain their market shares
Cartels + other collusion
Cartel - A group of producers that typically creates a formal written agreement specifying how much each member will produce and charge
Obstacles to collusion
Demand + cost differences - When oligopolists face different costs and demand curves, it is difficult for them to agree on a price
Number of firms - Other things equal, the larger the number of firms, the more difficult it is to create a cartel or some other form of price collusion
Cheating - Collusive oligopolists are tempted to engage in secret price cutting to increase sales and profit
Long-lasting recession - Slumping markets increase average total cost
Potential entry of new firms - The greater prices and profits that result from collusion may attract new entrants, including foreign firms
Anti-trust law - U.S. antitrust laws prohibit cartels and price-fixing collusion
Price leadership - The dominant firm initiates price changes and all other firms more or less automatically follow the leader
Infrequent price changes
Communications of price changes
Limit pricing
Oligopoly + advertising
Product development + advertising less easily duplicated than price cuts
Positive effects
Diminishes monopoly power
Lowers consumers’ search costs
More economic efficiency
Negative effects
No info about price or quality
Based on misleading claims
Establishes brand loyalty + monopoly power
Oligopoly + efficiency
Neither productive nor allocative efficiency
No regulation of loophole monopoly power
Chapter 11: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Monopolistic competition - Relatively large number of sellers, differentiated products, easy entry/exit
Relatively large # of sellers
Small market shares
No collusion - The presence of a relatively large number of firms ensures that collusion by a group of firms to restrict output and set prices is unlikely
Independent action - Each firm can determine its own pricing policy without considering the possible reactions of rival firms
Product differentiation - Variations of particular product
Product attributes
Service
Location
Brand names + packaging
Some control over product prices
Easy entry + exit
Few economies of scale
Low capital requirements
Non-price competition - Product differentiation + advertising
Four firm concentration ratio - Ratio of the output (sales) of the four largest firms in an industry relative to total industry sales
Very low in purely competitive industries
Herfindahl index - Sum of the squared percentage market shares of all firms in the industry
Important to assess oligopolistic industries
Lower index → Greater chance of being competitive
Monopolistic competition’s demand curve
Highly elastic
No perfect product substitutes
Price elasticity depends on # of rivals + degree of product differentiation
Short run
Produces where MR = MC
May incur loss in short run

Long run
Only normal profit (break even)
Economic profits → Firms enter industry → Quantity increases → Economic profit decreases
Economic losses → Firms leave industry → Quantity decreases → Economic profit increases
Complications
Product differentiation can prevent duplication
In reality, entry is not as free

Efficiency
Neither productive nor allocative efficiency
Average total cost slightly higher than optimal
P > MC → Underallocation of resources
Excess capacity - Plant and equipment that are underused because firms are producing less than the minimum-ATC output
Product differentiation
Stay ahead of competitors
Provides more range to consumers
Trade-off b/w consumer choice + productive efficiency
Oligopoly - Market dominated by a few large producers of a homogeneous or differentiated product
3-5 firms
Homogeneous oligopoly - Standardized products
Differentiated oligopoly - Differentiated products
Strategic behavior - Self-interested behavior that takes into account reactions of others
Mutual interdependence - A situation in which each firm’s profit depends not entirely on its own price and sales strategies but also on those of the other firms
Entry barriers
Economies of scale
Large capital expenditures
Ownership + control of raw resources
Merge 2 competing firms → Increase market share + achieve greater economies of scale + greater monopoly power
Shortcomings of concentration ratios
Localized markets
Interindustry competition - Competition b/w 2 products associated w/ different industries
Import competition - Competition b/w foreign products
Game theory - Study of how people behave in strategic situations
Payoff matrix shows payoff to each firm resulting from different combinations of strategies
Collusion - Cooperation w/ rivals rather than work competitively/independently
Incentive to cheat - Cheating on collusive agreement to increase own profit
3 oligopoly models
(1) the kinked-demand curve, (2) collusive pricing, and (3) price leadership
Why isn’t there only a single model?
Diversity of oligopolies - Oligopoly encompasses a greater range and diversity of market situations than do other market structures
Complications of interdependence - The mutual interdependence of oligopolistic firms complicates matters significantly
Kinked demand curve - Demand is highly elastic above the going price P0 but much less elastic or even inelastic below that price
Rivals can either match price changes or ignore price changes
Prices stable in non-collusive oligopolistic industries
Even if costs change significantly, may not need to change price
Price war - Successive and continuous rounds of price cuts by rivals as they attempt to maintain their market shares

Cartels + other collusion
Cartel - A group of producers that typically creates a formal written agreement specifying how much each member will produce and charge
Obstacles to collusion
Demand + cost differences - When oligopolists face different costs and demand curves, it is difficult for them to agree on a price
Number of firms - Other things equal, the larger the number of firms, the more difficult it is to create a cartel or some other form of price collusion
Cheating - Collusive oligopolists are tempted to engage in secret price cutting to increase sales and profit
Long-lasting recession - Slumping markets increase average total cost
Potential entry of new firms - The greater prices and profits that result from collusion may attract new entrants, including foreign firms
Anti-trust law - U.S. antitrust laws prohibit cartels and price-fixing collusion
Price leadership - The dominant firm initiates price changes and all other firms more or less automatically follow the leader
Infrequent price changes
Communications of price changes
Limit pricing
Oligopoly + advertising
Product development + advertising less easily duplicated than price cuts
Positive effects
Diminishes monopoly power
Lowers consumers’ search costs
More economic efficiency
Negative effects
No info about price or quality
Based on misleading claims
Establishes brand loyalty + monopoly power
Oligopoly + efficiency
Neither productive nor allocative efficiency
No regulation of loophole monopoly power
 Knowt
Knowt
