
Bio H DNA Transcription + Translation
Transcription- when an mRNA copy of a gene is made from DNA
A gene- a sequence of nucleotides on a strand of DNA that codes for one protein
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid
Differences between RNA and DNA
RNA has a ribose for a sugar instead of a deoxyribose
RNAs bases are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil (NO THYMINE!)
RNA has only 1 strand where DNA has two
What does RNA do? It depends on the type! there are 3 (and more, but whatevs) kinds of RNA
3 types of RNA=
mRNA is a copy of a gene that goes from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosome
tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA combines with proteins to make a ribosome
Amino acids= monomers that make proteins, pre-protein
Ribosomes are the machines that make the proteins.
Animation time yaaay
The red is a strain of DNA. The proteins are attached to the DNA because they have something that is chemically attracted to a specific part of the DNA. Other proteins do the same thing and make a lump. Enzymes are made out of proteins. There is a skiing analogy I forgot. When things chemically bond its usually covalent because covalent bonds are so strong. This was figured out by Crick. The proteins are just hanging when othen proteins attach to them kinda like iron man. The mRNA breaks down the DNA and a bunch of nucleotides are floating around and getting sucked in in the right order and then it hits a sequence of DNA that tells it to stop called a sequence DNA and the mRNA goes away.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TfYf_rPWUdY- mRNA translation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMtWvDbfHLo- DNA transcription
DNALC Short: Transcription and Translation
Step by Step of transcription
Step 1. Transcription factors are attracted by a specific nucleotide sequence.
Step 2. Other proteins attach to the transcription factors to make a large starting place for RNA polymerase, which is the enzyme that is going to build the mRNA strand. The process requires an activation protein. The protein is like the spark. It gets pulled over by chemical attraction and when they touch its the start.
Step 3. Once the RNA polymerase is in place, it starts down the gene (DNA strand). It needs help to start moving. (The first 23 nucleotides.)
Step 4. The RNA polymerase builds the mRNA strand by putting RNA nucleotides together in the right order.
DNA RNA (remember, no T!)
A U--
T A | Codone
C G--
G C
T A
A U
They are read as groups of 3, called codones. Those match anti codones on the other side of the DNa. The order of the codones determines the order of the amino acids.
Transcription has 3 steps
Initiation
: During initiation the protein complexes assemble from TF(transcription factor). The TF helps start the RNA polymerase (ase denotes its an enzyme, ose means its a sugar. not all proteins end in ASE but everything with ase is a protein). The TF also opens the transcription bubble. A transcription bubble is where transcription takes place. Many DNA stays put. The DNA is twisted so it would be inefficient to completly unravel it but a portion opens up and that’s a transcription bubble. As soon as its done with the polymerase is closes again
Elongation
When the mRNA is made. What happens here is that the RNA polymerase moves down 1 strand of DNA and reads the sequence of nucleotides. So then as it reads the sequence it puts together an mRNA strand that has the complimentary sequence of RNA nucleotides. V
DNA TACCCGTTAGCG
mRNA AUGGGCAAUCGC
Its not the same, its the one that matches. It always starts with TAC and AUG because thats the sequence that tells it to start and its the amino acid. Theres 4 different possibilites.
Elongation continues until a termination sequence of DNA nucleotides is encountered. If the gene has 200 nucleotides thats how long it goes, etc for any number. Some can have 100,000!
Termination
The RNA polymerase reads a termination sequence and stops reading the nucleotides. The mRNA strand that was put together by the RNA polymerase breaks free and exits the nucleis to find a ribosome. Transcription is just the process where they make mRNA. If the DNa breaks you cant make your proteins and the cell dies so we protect it so we use the mRNA because if the mRNA breaks we can make a copy and it’s ok.
Translation
You need to understand a ribosome first. A stupid hokey poker joke was made here and then a funny joke was made.
A ribosome has 2 parts
The first part looks like a silly liyyle pacman ghost and the other part is a circle under it. These are organelles The ghost is called the Large sub-ubit and the oval is called a small sub-unit. The little divits make an EPA and the oval is made from proteins and rRNA. Ribosome reads the code on the mRNa and turnes it into a protein.
tRNA looks like a dorito with bug legs.
The top point is an amino acid. It is a single strand like DNA, but its wound up into a triangle. for example, UAC are at the bottom and are called an anticodone. Transfer RNA, or tRNA. There are 20 amino acids. The one at the tip of the top point is only 1 of 20 there. Whatever the anti codone is it will only hold a certain type of amino acid. 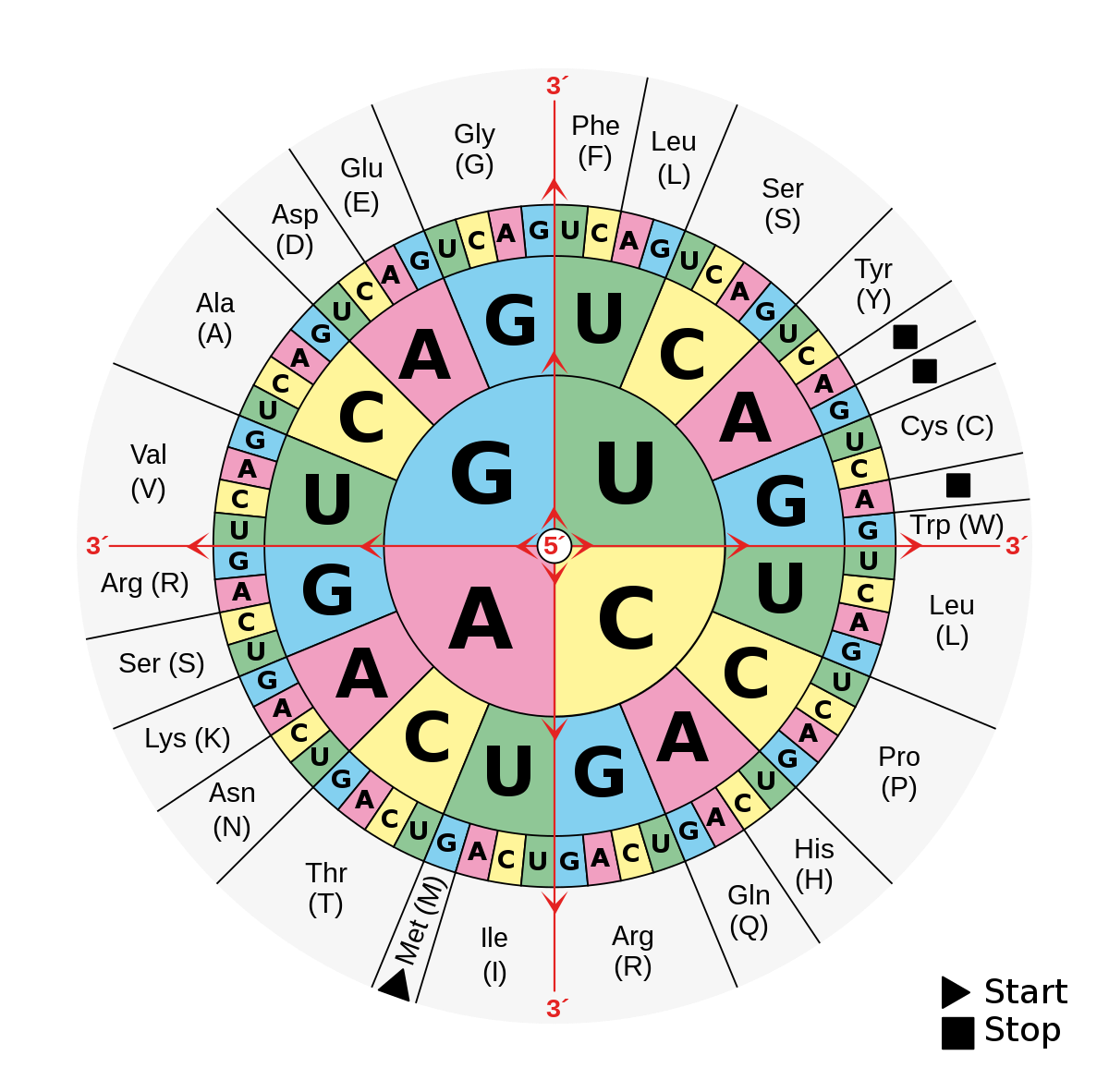
on the outside are all the Amino acids. The IN comes from the fact is an amINo acid group. haha. The mRNA is broken up into groups of 3 called codons and it matches with the anticodone and form a temporary hydrogen bond and move and it releases the amino acid and thats how they fit together. For the chart you only use CODONs and not anticodons. From the DNA you can find the codone which tells the tRNA to release Amino acids they move to the ribosome. mRNA is the longest.
The black squares means stop and it tells the process to stop and that its done making the protein and the chain breaks free and is a finished protein. Its called a redundancy when one protein can be made by multiple combinations.
What happens in the ribosome
The mRNA leaves the nucleis and finds a ribosome somehow (there are a lot in the cell) Any ribosome can make any protein so as long as the mRNA finds a ribosome it can make it. The mRNA finds it and shifts over so that the codon to start is at the A site. Then a bunch of tRNAs are floating and at the top are amino acids and so the tRNA is pulled in and goes to the codones and if it matches it and forms a bond then it all shifts one place so they are now at the P site and at the A site. If it doesnt then its kicked out and they find another tRNA. When its at the P spot it goes through a tube and breaks the bond and goes out the top. The codon shifts again to the E site and is ejected from the rRNA. Thats why its called the E site and the amino acid pees itself (it forms a peptide chain). After a while theres a bunch of amino acids and thats the peptide chain. The acids are attracted to eachother and thats why it forms and the chain bends in weird ways. When its done bending it has a very specific shape and thats what makes it a protein. We don’t know all the shapes but if you did it would make awesome medicine. When the stop signal goes it stops and the enzymes tear apart the mRNA and and is recylceded
Mutations
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. It can be a mistake during replication or it can be a mistake in the DNA polymerase putting the nucleis in the wrong place. It can also be cause by something. Substitution is when only one nucleotide is changed. It is shown below. Mutations can be the cause of cancer, and instead of a mutagen its called a canceragen.
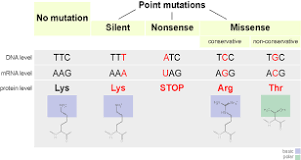
A frameshift mutation is caused by a mutagen and is a deletion or insertion. Deletion is when you delete a nucleotide and all of the codons shift so they are all coding for something else. An insertion is where you add a nucleotide instead, but the result is relatively the same.
Bio H DNA Transcription + Translation
Transcription- when an mRNA copy of a gene is made from DNA
A gene- a sequence of nucleotides on a strand of DNA that codes for one protein
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid
Differences between RNA and DNA
RNA has a ribose for a sugar instead of a deoxyribose
RNAs bases are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil (NO THYMINE!)
RNA has only 1 strand where DNA has two
What does RNA do? It depends on the type! there are 3 (and more, but whatevs) kinds of RNA
3 types of RNA=
mRNA is a copy of a gene that goes from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosome
tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA combines with proteins to make a ribosome
Amino acids= monomers that make proteins, pre-protein
Ribosomes are the machines that make the proteins.
Animation time yaaay
The red is a strain of DNA. The proteins are attached to the DNA because they have something that is chemically attracted to a specific part of the DNA. Other proteins do the same thing and make a lump. Enzymes are made out of proteins. There is a skiing analogy I forgot. When things chemically bond its usually covalent because covalent bonds are so strong. This was figured out by Crick. The proteins are just hanging when othen proteins attach to them kinda like iron man. The mRNA breaks down the DNA and a bunch of nucleotides are floating around and getting sucked in in the right order and then it hits a sequence of DNA that tells it to stop called a sequence DNA and the mRNA goes away.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TfYf_rPWUdY- mRNA translation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMtWvDbfHLo- DNA transcription
DNALC Short: Transcription and Translation
Step by Step of transcription
Step 1. Transcription factors are attracted by a specific nucleotide sequence.
Step 2. Other proteins attach to the transcription factors to make a large starting place for RNA polymerase, which is the enzyme that is going to build the mRNA strand. The process requires an activation protein. The protein is like the spark. It gets pulled over by chemical attraction and when they touch its the start.
Step 3. Once the RNA polymerase is in place, it starts down the gene (DNA strand). It needs help to start moving. (The first 23 nucleotides.)
Step 4. The RNA polymerase builds the mRNA strand by putting RNA nucleotides together in the right order.
DNA RNA (remember, no T!)
A U--
T A | Codone
C G--
G C
T A
A U
They are read as groups of 3, called codones. Those match anti codones on the other side of the DNa. The order of the codones determines the order of the amino acids.
Transcription has 3 steps
Initiation
: During initiation the protein complexes assemble from TF(transcription factor). The TF helps start the RNA polymerase (ase denotes its an enzyme, ose means its a sugar. not all proteins end in ASE but everything with ase is a protein). The TF also opens the transcription bubble. A transcription bubble is where transcription takes place. Many DNA stays put. The DNA is twisted so it would be inefficient to completly unravel it but a portion opens up and that’s a transcription bubble. As soon as its done with the polymerase is closes again
Elongation
When the mRNA is made. What happens here is that the RNA polymerase moves down 1 strand of DNA and reads the sequence of nucleotides. So then as it reads the sequence it puts together an mRNA strand that has the complimentary sequence of RNA nucleotides. V
DNA TACCCGTTAGCG
mRNA AUGGGCAAUCGC
Its not the same, its the one that matches. It always starts with TAC and AUG because thats the sequence that tells it to start and its the amino acid. Theres 4 different possibilites.
Elongation continues until a termination sequence of DNA nucleotides is encountered. If the gene has 200 nucleotides thats how long it goes, etc for any number. Some can have 100,000!
Termination
The RNA polymerase reads a termination sequence and stops reading the nucleotides. The mRNA strand that was put together by the RNA polymerase breaks free and exits the nucleis to find a ribosome. Transcription is just the process where they make mRNA. If the DNa breaks you cant make your proteins and the cell dies so we protect it so we use the mRNA because if the mRNA breaks we can make a copy and it’s ok.
Translation
You need to understand a ribosome first. A stupid hokey poker joke was made here and then a funny joke was made.
A ribosome has 2 parts
The first part looks like a silly liyyle pacman ghost and the other part is a circle under it. These are organelles The ghost is called the Large sub-ubit and the oval is called a small sub-unit. The little divits make an EPA and the oval is made from proteins and rRNA. Ribosome reads the code on the mRNa and turnes it into a protein.
tRNA looks like a dorito with bug legs.
The top point is an amino acid. It is a single strand like DNA, but its wound up into a triangle. for example, UAC are at the bottom and are called an anticodone. Transfer RNA, or tRNA. There are 20 amino acids. The one at the tip of the top point is only 1 of 20 there. Whatever the anti codone is it will only hold a certain type of amino acid. 
on the outside are all the Amino acids. The IN comes from the fact is an amINo acid group. haha. The mRNA is broken up into groups of 3 called codons and it matches with the anticodone and form a temporary hydrogen bond and move and it releases the amino acid and thats how they fit together. For the chart you only use CODONs and not anticodons. From the DNA you can find the codone which tells the tRNA to release Amino acids they move to the ribosome. mRNA is the longest.
The black squares means stop and it tells the process to stop and that its done making the protein and the chain breaks free and is a finished protein. Its called a redundancy when one protein can be made by multiple combinations.
What happens in the ribosome
The mRNA leaves the nucleis and finds a ribosome somehow (there are a lot in the cell) Any ribosome can make any protein so as long as the mRNA finds a ribosome it can make it. The mRNA finds it and shifts over so that the codon to start is at the A site. Then a bunch of tRNAs are floating and at the top are amino acids and so the tRNA is pulled in and goes to the codones and if it matches it and forms a bond then it all shifts one place so they are now at the P site and at the A site. If it doesnt then its kicked out and they find another tRNA. When its at the P spot it goes through a tube and breaks the bond and goes out the top. The codon shifts again to the E site and is ejected from the rRNA. Thats why its called the E site and the amino acid pees itself (it forms a peptide chain). After a while theres a bunch of amino acids and thats the peptide chain. The acids are attracted to eachother and thats why it forms and the chain bends in weird ways. When its done bending it has a very specific shape and thats what makes it a protein. We don’t know all the shapes but if you did it would make awesome medicine. When the stop signal goes it stops and the enzymes tear apart the mRNA and and is recylceded
Mutations
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. It can be a mistake during replication or it can be a mistake in the DNA polymerase putting the nucleis in the wrong place. It can also be cause by something. Substitution is when only one nucleotide is changed. It is shown below. Mutations can be the cause of cancer, and instead of a mutagen its called a canceragen.

A frameshift mutation is caused by a mutagen and is a deletion or insertion. Deletion is when you delete a nucleotide and all of the codons shift so they are all coding for something else. An insertion is where you add a nucleotide instead, but the result is relatively the same.
 Knowt
Knowt
